Creating content everyone can use isn’t just thoughtful—it’s essential. While we often focus on making our material engaging and informative, it’s equally important to ensure it’s usable by all individuals, including those with disabilities. This article explores why accessible content matters in content creation and offers practical steps to make content more inclusive.
Understanding accessibility
Accessibility in content creation means crafting information everyone can use and understand, regardless of their abilities or limitations. This approach considers the needs of people with various challenges, such as those who have trouble seeing, hearing, moving, or processing information. By designing with accessibility in mind, we ensure that our content reaches and serves a diverse audience, including those who might otherwise be left out.
Why accessibility is important
Broadening your audience
Making your content accessible allows you to reach a wider audience. When you consider accessibility in your design, more individuals can interact with your content, potentially expanding your reach and influence. This could lead to increased website traffic, more customers, and higher sales for businesses.
- Statistic: A study found that 71% of users with disabilities will leave an inaccessible website, leading to an estimated $6.9 billion in potential e-commerce sales lost in the U.S. alone (Source: “Click-Away Pound Survey,” 2019).
Moreover, accessible content often benefits everyone, not just those with disabilities. For instance, adding captions to videos helps not only people who are deaf or hard of hearing but also anyone in a noisy environment or who prefers reading along.
Legal obligations
Many countries have laws requiring digital content to be accessible to prevent discrimination against people with disabilities. Ignoring these requirements can lead to legal issues, including fines and lawsuits.
- Statistic: In the United States, lawsuits related to digital accessibility under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) increased by 23% from 2019 to 2020, highlighting the growing legal risks (UsableNet ADA Website Accessibility Lawsuit Report, 2020).
By complying with accessibility laws such as the ADA in the U.S. or the Equality Act in the U.K., organizations avoid legal repercussions and demonstrate respect and inclusivity toward all users.
Enhancing brand reputation
Prioritizing accessibility can improve how people perceive your brand. It shows that you value inclusivity and social responsibility, which can resonate positively with consumers. Many customers prefer to support brands that align with their values.
- Statistic: According to a study by Accenture, 62% of consumers prefer to buy from companies that take a stand on issues like inclusion and diversity (Accenture, “From Me to We: The Rise of the Purpose-Led Brand,” 2018).
By focusing on accessibility, you signal that you care about all your customers, potentially fostering long-term trust and loyalty.
Key principles for accessible content
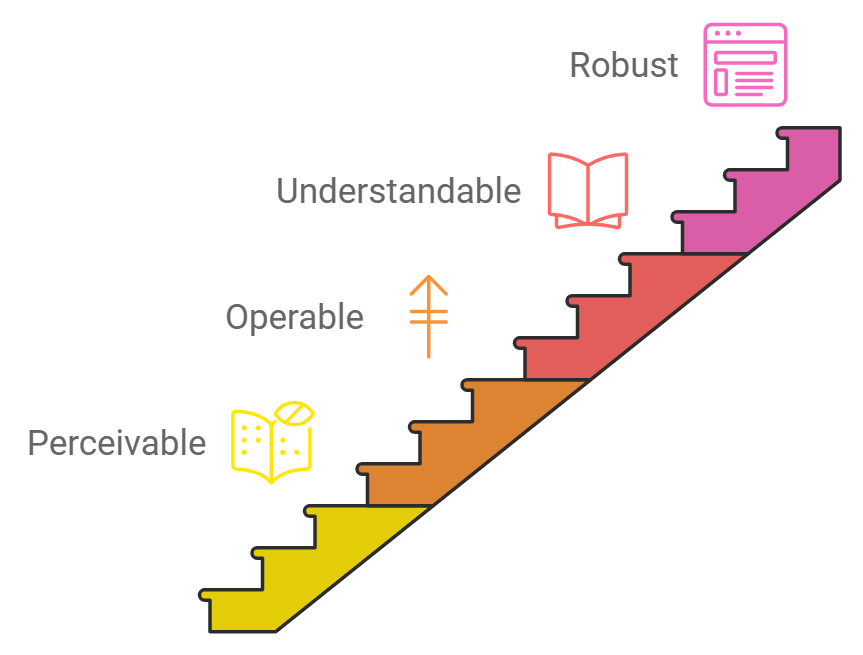
To make your content accessible, consider these core principles:
- Perceivable: Present information in ways that everyone can perceive. Provide text alternatives for images, offer video captions, and ensure your content isn’t dependent on colour alone. Example: Use descriptive alt text for images so that screen readers can convey the information to users who cannot see them.
- Operable: Ensure that all users can navigate and interact with your content. Ensure all functionality is available from a keyboard, give users enough time to read and use content, and avoid elements that could cause seizures. Example: Verify that people can navigate your website using a keyboard, not just a mouse or touch screen.
- Understandable: Make your content clear and easy to comprehend. Use simple language, explain complex terms, and maintain consistent navigation. Example: Write in plain language to help users with cognitive disabilities easily understand your content.
- Robust: Build your content to work with various technologies, including assistive devices. Use proper coding practices and test your content with different browsers and tools. Example: Ensure your website’s code adheres to web standards so screen readers and other assistive technologies can correctly interpret it.
By following these principles, you’ll make your content more accessible and enhance the user experience for everyone.
Practical tips to enhance accessibility
Improving the accessibility of your content can be straightforward with these steps:
- Use clear language: Write in a simple and direct manner to make your content easy to understand. Short sentences and common words help readers grasp your message quickly.
- Describe images: Provide text descriptions so screen readers can convey them to users who cannot see them. The descriptions should be concise yet informative. Example: Instead of “Image of a chart,” write “Bar chart showing a 20% increase in sales over the past year.”
- Organize content with headings: Use headings and subheadings to structure your content, making it easier to navigate. Properly structured headings allow users with screen readers to scan your content efficiently.
- Ensure keyboard navigation: Make sure users can navigate your site using a keyboard alone. This is crucial for people who cannot use a mouse. Test: Navigate your website using only the Tab and Enter keys to ensure all interactive elements are accessible.
- Add transcripts and captions: Provide transcripts for audio content and captions for videos. This assists users who are deaf or hard of hearing and benefits non-native speakers.
- Use contrasting colours: Ensure sufficient contrast between text and background colours so that users with visual impairments can read your content. Guideline: Follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) recommendation for contrast ratios (WCAG Contrast Guidelines).
- Make links descriptive: Use clear and descriptive text for links that indicate where the link will take the user. Avoid phrases like “click here.”Example: Use “Learn more about our accessibility features” instead of “Click here to learn more.”
- Avoid flashing content: Steer clear of flashing elements, as they can trigger seizures in people with photosensitive epilepsy. Guideline: Content should not flash more than three times in any one second (WCAG Guidelines on Flashing Content).
- Test your content: Utilize tools to check the accessibility of your content and consider having it tested by people with disabilities to identify areas for improvement. Tools: Accessibility evaluation tools like WAVE or Axe can help identify issues.
By implementing these steps, you’ll make significant progress toward making your content accessible to everyone.
Companies setting an example
Apple
Apple incorporates accessibility features across its products, such as VoiceOver for screen reading, Zoom for magnification, and Switch Control for adaptive use. It continuously innovates to ensure its devices can be used by as many people as possible.
- Learn more: Apple Accessibility.
Microsoft
Microsoft has developed an Inclusive Design Toolkit to help create products everyone can use. They offer features like Immersive Reader, which aids users with reading difficulties, and Seeing AI, an app that narrates the world for those who are blind or have low vision.
- Learn more: Microsoft Inclusive Design.
Shopify
Shopify emphasizes accessibility by providing themes and tools that help merchants build online stores accessible to all users. It also offers guidelines and best practices to support inclusive e-commerce.
- Learn more: Shopify Accessibility Guidelines.
Government digital services
Several governments, such as the U.K.’s Government Digital Service, have developed design systems that prioritize accessibility. Their design principles and components are open-source, helping others incorporate accessible design into their projects.
- Learn more: GOV.UK Design System.
These organizations demonstrate that focusing on accessibility leads to better products and services that benefit everyone.
The business benefits
Investing in accessibility isn’t just the right thing to do—it’s also advantageous for your business.
- Statistic: A report by Accenture revealed that companies leading in disability inclusion had, on average, 28% higher revenue and two times the net income over a four-year period compared to others in their industry (Accenture, “Getting to Equal: The Disability Inclusion Advantage,” 2018).
By making your content accessible, you’re opening your business to a broader market and building customer loyalty. Accessible websites often perform better in search engine rankings due to improved usability and structure.
- SEO benefit: Accessible websites may rank higher in search results because of better user experience and adherence to best practices (Search Engine Journal, “How Web Accessibility Affects SEO,” 2020).
Additionally, designing for accessibility can lead to innovation. Businesses can develop new products and services that provide a competitive edge by meeting diverse user needs.
- An example of innovation is voice-controlled interfaces, which were initially developed to assist users with mobility impairments but have become popular among many users for their convenience.
Conclusion
Accessibility is a vital aspect of creating content that serves everyone. Ensuring your content can be used by all people meets legal requirements, expands your audience, and enhances your brand’s reputation. By adopting accessible practices, you’re contributing to a more inclusive world. Small changes can make a big difference. Start incorporating accessibility into your content today, and you’ll positively impact your audience and your business. Prioritizing accessibility shows that you value every individual, which can build trust and loyalty. This commitment can set your brand apart as a leader in inclusivity. Take action now. Review your current content, apply these practical tips, and help create a more accessible and equitable digital space for everyone.
